Modeling is the process of creating a representation of an object, system, or environment. It involves using various techniques and tools to design, shape, and refine a model, which can be used for a variety of purposes such as visualization, simulation, analysis, or production.
Key Concepts in 3D Modeling
Three-dimensional objects are entities that have length, width, and depth. They can be natural, such as mountains or trees, or man-made, such as buildings or bridges. In the context of 3D modeling, three-dimensional objects are the subjects of creation and manipulation.
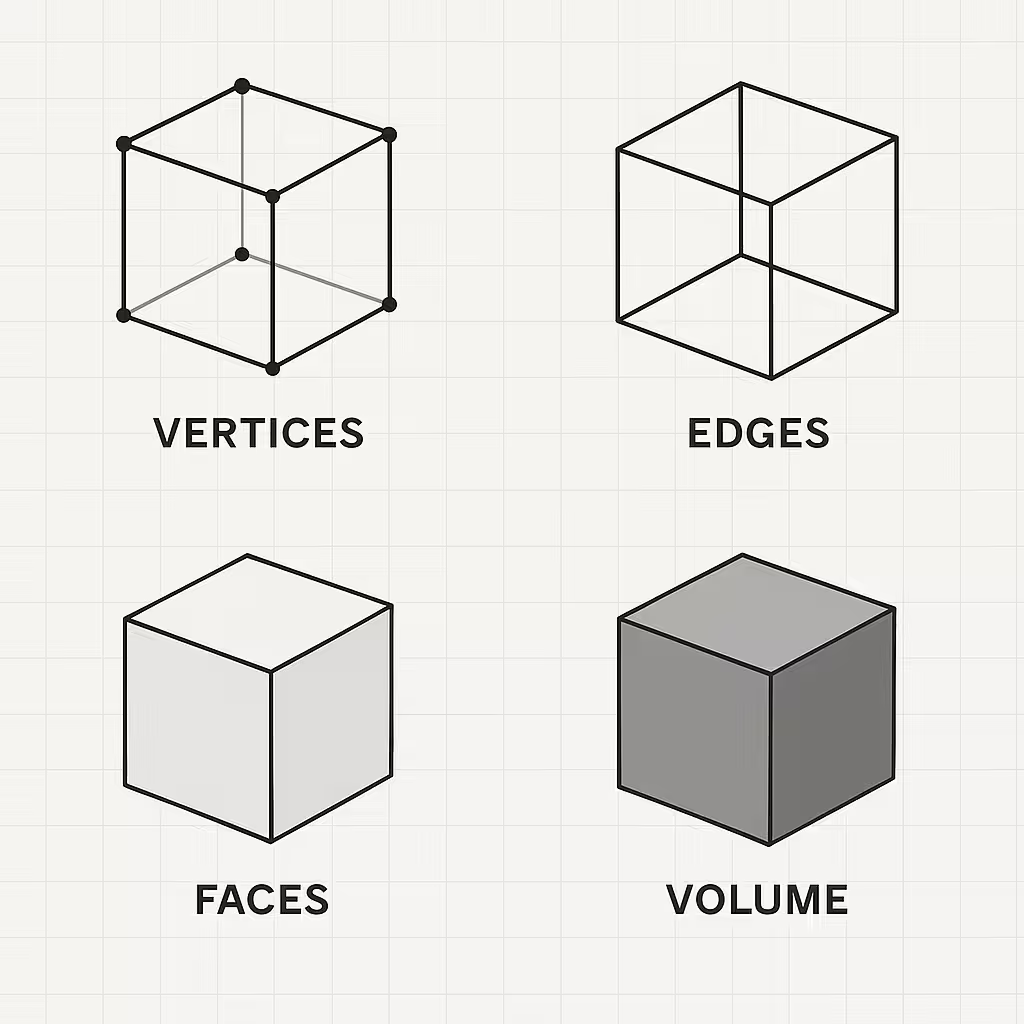
Vertices, Edges, Faces, Volume
- Coordinates: Coordinates are a set of numbers that define the position of a point in space. In 3D modeling, - - coordinates can refer to the x, y, and z coordinates of a point in 3D space, which can be used to locate and measure objects and features.
- Vertices: Vertices are the points in 3D space that define the shape of an object. They are connected by edges to form the object’s geometry.
- Edges: Edges are the lines that connect vertices to form the shape of an object.
- Faces: Faces are the surfaces of an object, defined by a set of vertices and edges.
- Volumes: Volumes refer to the amount of space inside a three-dimensional shape, such as a cube. In 3D modeling, volumes are used to calculate the size and proportions of objects, and can be used to simulate real-world physics and behavior.
3D Modeling Techniques
Non exhaustive list.
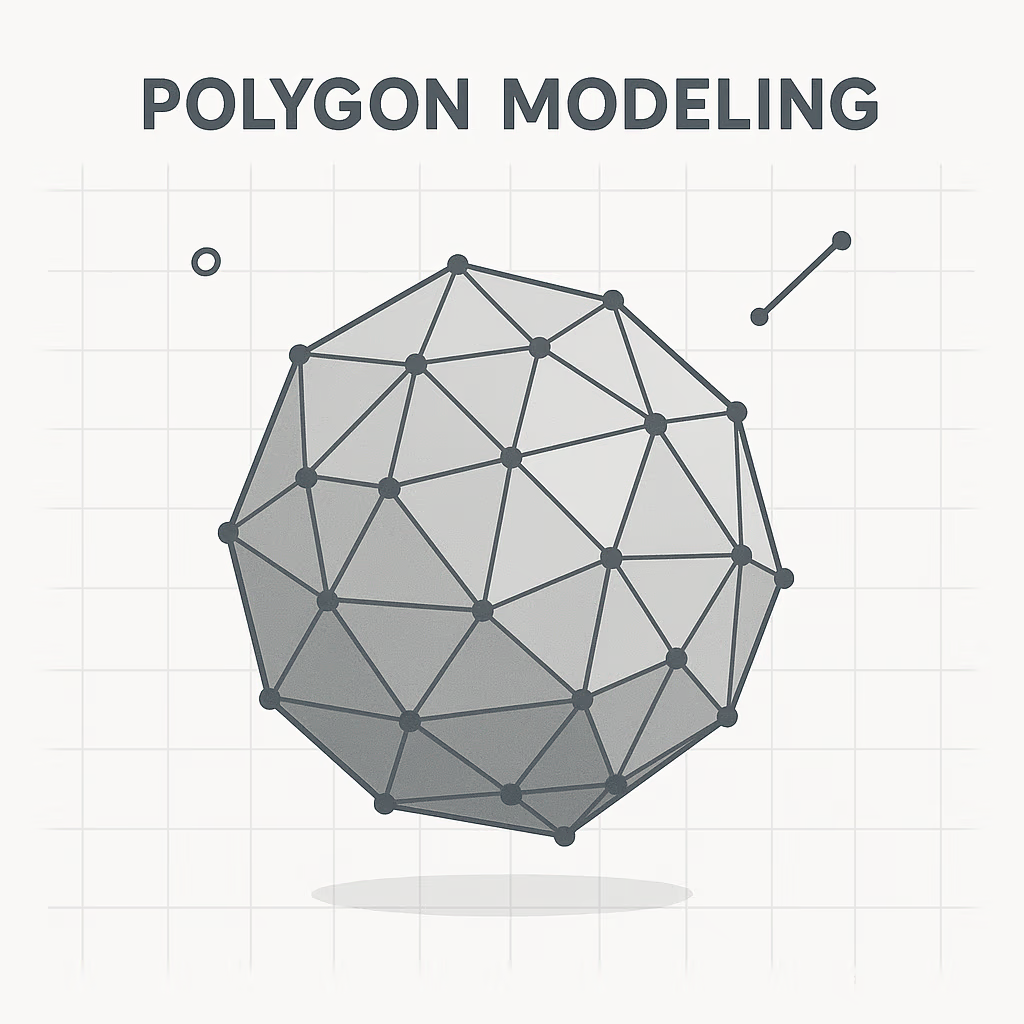
Polygon modelling
- Polygon Modeling: Polygon modeling is a technique used to create 3D models by connecting vertices to form polygons.
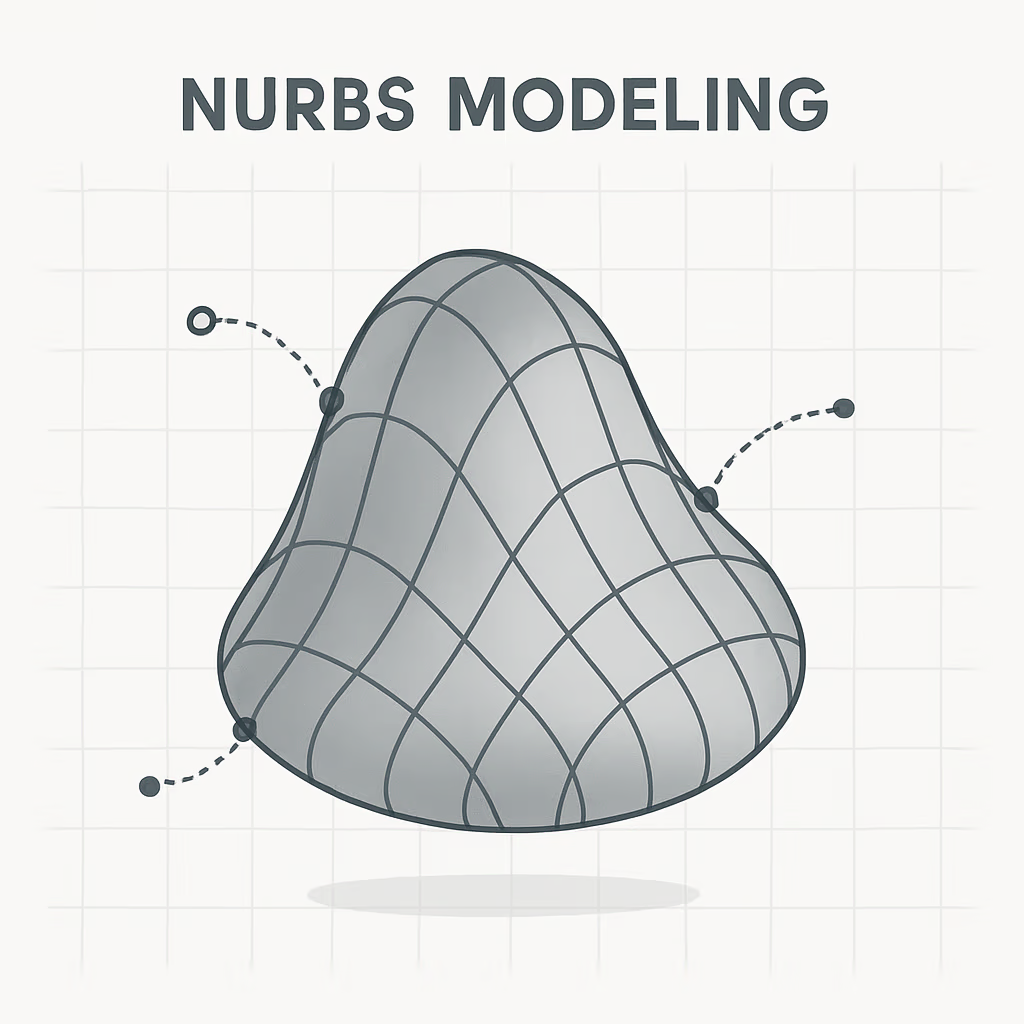
NURBs modelling
- NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines) Modeling: NURBS modeling is a technique used to create smooth, curved surfaces using mathematical equations.
- Sculpting: Sculpting is a technique used to create 3D models by shaping and molding a digital clay-like material.
- Parametric Modeling: Parametric modeling is a technique used to create 3D models using mathematical equations and parameters, allowing for easy modification and iteration.
- Subdivision Surface Modeling: Subdivision surface modeling is a technique used to create smooth, curved surfaces by subdividing a polygon mesh into smaller, more detailed surfaces.
- Procedural Modeling: Procedural modeling is a technique used to create 3D models using algorithms and procedures, allowing for the creation of complex, detailed models with minimal user input.
- Digital Elevation Modeling (DEM): DEM is a technique used to create 3D models of terrain and landscapes using elevation data.